An Solar Inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC); the converted AC can be at any required voltage and frequency with the use of appropriate transformers, switching, and control circuits. A Solar Inverter changes DC voltage from batteries or solar panels, into standard household AC voltage so that it can be used by common tools and appliances.There has Two type Solar inverter: off-grid inverter (stand-alone Inverter),and Grid tied inverter ( Grid Connected Inverter).
off-grid inverter (stand-alone Inverter)
Off-grid inverter or Stand-alone inverter is designed for remote stand-alone application or off-grid power system with battery backup where the inverter draws its DC power from batteries charged by PV array and converts to AC power. Stand-alone inverters provide variety of size and output waveform depending on your applications. For the best output, the pure sine inverter is required. It suits for solar home system, rural electrification, village electrification in remote area where the utility grid is not available.
Grid tied inverter ( Grid Connected Inverter)
Grid connected inverter or grid tie inverter is designed specifically for grid connected application that does not require battery backup system. Grid connected inverter or grid tie inverter converts DC power produced by PV array to AC power to supply to electrical appliances and sell excess power back to utility grid. With a range of sizes available, we provide grid tie inverter to suit your needs, from small residential solar system to large commercial solar system.
What is the difference between Pure Sine wave and Modified or Square Sinewave Inverter?
The simple answer
This can get complicated but the easiest way to compare waveforms is like comparing them to petrol – a pure sinewavpe is like Optimax and a modified sinewave is like regular unleaded. Use a pure sinewave UPS on your expensive equipment (i.e. servers) and save the modified sinewave for cheap equipment (i.e. PC Workstations).
The detailed answer
When electricty is produced and delivered to your premises it arrives in as alternating current (AC) and as such has an alternating waveform (DC power does not have a waveform). When UPS were first invented they were designed to mimic and output this pure waveform after they cleaned up the original waveform. As time went on and everything started getting cheaper design engineers (and their bosses) discovered that they could save money and build a cheaper UPS by using less complicated UPS components (mainly the inverter) by having it output a sinewave that wasn’t quite as perfect as the true version – it would look more like a series of steps rather than a curve. Since that time many manufactures have opted to produce modified or square wave UPS systems for low end equipment.
Using a modified sinewave UPS is generally not a problem for low end equipment as most switch mode power supplies like the ones found in your PC don’t mind the square wave, even though they were designed to run on a pure sinewave. Problems start however when you start using them with more sensitive equipement. Anything with a transformer in it won’t work to start with. Higher end systems may dislike the power supply and function (or disfunction) accordingly.
The other problem with simulated sinewaves is that they can cause equipment they power to to run hotter than normal which can shorten the lifespan of the power supply. This is generally ok with a workstation or PC where the power supply only costs $50-60 but it will be concern in a server grade system where the replacment costs ( let alone the down time expenses) are much higher. The other drama with modifed sinewave UPS is that they are less efficient, as more energy is used up to deliver the same result. For example a 1kVA simulated sinewave UPS with the same battery as a 1kVA pure sinewave UPS will provide less backup time in the event of a power failure.
EPEVER Solar Inverter
Features:
·Complete isolation-type inverter technology, noiseless output
·Adoption of advanced SPWM technology, pure sine wave output
·Dynamic current loop control technology to ensure inverter reliable operation.
·Wide DC input voltage range
·Excellent EMC design
·Low output harmonic distortion(THD≤3%)
·LED indicators display input voltage range, load power range, normal output & failure state
·Optional energy saving mode
·Wide working temperature range (industrial level)
·Continuous operation at full power
Protections:
·Output Short Circuit
·Overload
·Input reverse polarity
·Input low voltage
·Input over voltage
·Inverter abnormal protection
·Overheating
Solar Inverter
An Solar Inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC); the converted AC can be at any required voltage and frequency with the use of appropriate transformers, switching, and control circuits. A Solar Inverter changes DC voltage from batteries or solar panels, into standard household AC voltage so that it can be used by common tools and appliances.There has Two type Solar inverter: off-grid inverter (stand-alone Inverter),and Grid tied inverter ( Grid Connected Inverter).
Off-grid inverter or Stand-alone inverter is designed for remote stand-alone application or off-grid power system with battery backup where the inverter draws its DC power from batteries charged by PV array and converts to AC power. Stand-alone inverters provide variety of size and output waveform depending on your applications. For the best output, the pure sine inverter is required. It suits for solar home system, rural electrification, village electrification in remote area where the utility grid is not available.
Grid connected inverter or grid tie inverter is designed specifically for grid connected application that does not require battery backup system. Grid connected inverter or grid tie inverter converts DC power produced by PV array to AC power to supply to electrical appliances and sell excess power back to utility grid. With a range of sizes available, we provide grid tie inverter to suit your needs, from small residential solar system to large commercial solar system.
What is the difference between Pure Sine wave and Modified or Square Sinewave Inverter?
The simple answer
This can get complicated but the easiest way to compare waveforms is like comparing them to petrol – a pure sinewavpe is like Optimax and a modified sinewave is like regular unleaded. Use a pure sinewave UPS on your expensive equipment (i.e. servers) and save the modified sinewave for cheap equipment (i.e. PC Workstations).
The detailed answer
When electricty is produced and delivered to your premises it arrives in as alternating current (AC) and as such has an alternating waveform (DC power does not have a waveform). When UPS were first invented they were designed to mimic and output this pure waveform after they cleaned up the original waveform. As time went on and everything started getting cheaper design engineers (and their bosses) discovered that they could save money and build a cheaper UPS by using less complicated UPS components (mainly the inverter) by having it output a sinewave that wasn’t quite as perfect as the true version – it would look more like a series of steps rather than a curve. Since that time many manufactures have opted to produce modified or square wave UPS systems for low end equipment.
Using a modified sinewave UPS is generally not a problem for low end equipment as most switch mode power supplies like the ones found in your PC don’t mind the square wave, even though they were designed to run on a pure sinewave. Problems start however when you start using them with more sensitive equipement. Anything with a transformer in it won’t work to start with. Higher end systems may dislike the power supply and function (or disfunction) accordingly.
The other problem with simulated sinewaves is that they can cause equipment they power to to run hotter than normal which can shorten the lifespan of the power supply. This is generally ok with a workstation or PC where the power supply only costs $50-60 but it will be concern in a server grade system where the replacment costs ( let alone the down time expenses) are much higher. The other drama with modifed sinewave UPS is that they are less efficient, as more energy is used up to deliver the same result. For example a 1kVA simulated sinewave UPS with the same battery as a 1kVA pure sinewave UPS will provide less backup time in the event of a power failure.
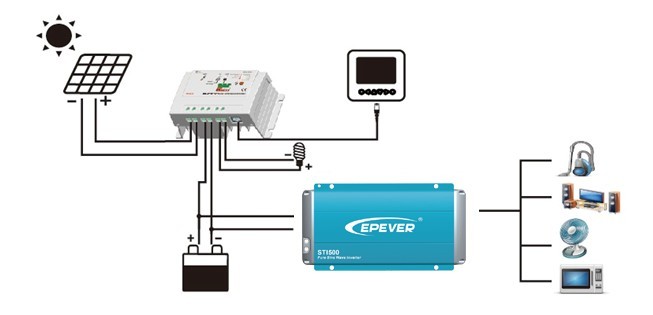
EPEVER Solar Inverter
Features:
·Complete isolation-type inverter technology, noiseless output
·Adoption of advanced SPWM technology, pure sine wave output
·Dynamic current loop control technology to ensure inverter reliable operation.
·Wide DC input voltage range
·Excellent EMC design
·Low output harmonic distortion(THD≤3%)
·LED indicators display input voltage range, load power range, normal output & failure state
·Optional energy saving mode
·Wide working temperature range (industrial level)
·Continuous operation at full power
Protections:
·Output Short Circuit
·Overload
·Input reverse polarity
·Input low voltage
·Input over voltage
·Inverter abnormal protection
·Overheating
Specification: